Can Brain Scans Detect Mental Illness? Exploring the Potential of Neuroimaging in Psychiatry
Mental illness affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing immense suffering and disability. Traditional methods of diagnosis and treatment often rely on subjective assessments and lack objective biomarkers. Neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and electroencephalography (EEG), offer a promising avenue for detecting mental illness by providing insights into the brain's structure, function, and connectivity.
Understanding Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is a non-invasive technique that allows researchers and clinicians to visualize and study the brain's structure and activity. Different neuroimaging techniques measure various aspects of brain function, including blood flow, metabolism, and electrical activity.
- fMRI: Measures changes in blood flow in the brain, which is indirectly related to neuronal activity.
- PET: Uses radioactive tracers to measure brain metabolism and neurotransmitter activity.
- EEG: Records electrical activity on the scalp, providing information about brain waves and neural oscillations.
Neuroimaging In Mental Illness Detection
Neuroimaging studies have shown promise in detecting mental illnesses, including schizophrenia, depression, and bipolar disorder. Researchers have identified patterns of brain abnormalities associated with these disorders, such as altered brain structure, decreased activity in certain brain regions, and abnormal connectivity between brain networks.
- Schizophrenia: Neuroimaging studies have found reduced brain volume in certain brain regions, such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, in individuals with schizophrenia.
- Depression: Neuroimaging studies have shown decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex and increased activity in the amygdala, a brain region involved in fear and emotional processing, in individuals with depression.
- Bipolar Disorder: Neuroimaging studies have found abnormalities in the brain's reward system and mood-regulating circuits in individuals with bipolar disorder.
Applications Of Neuroimaging In Psychiatry
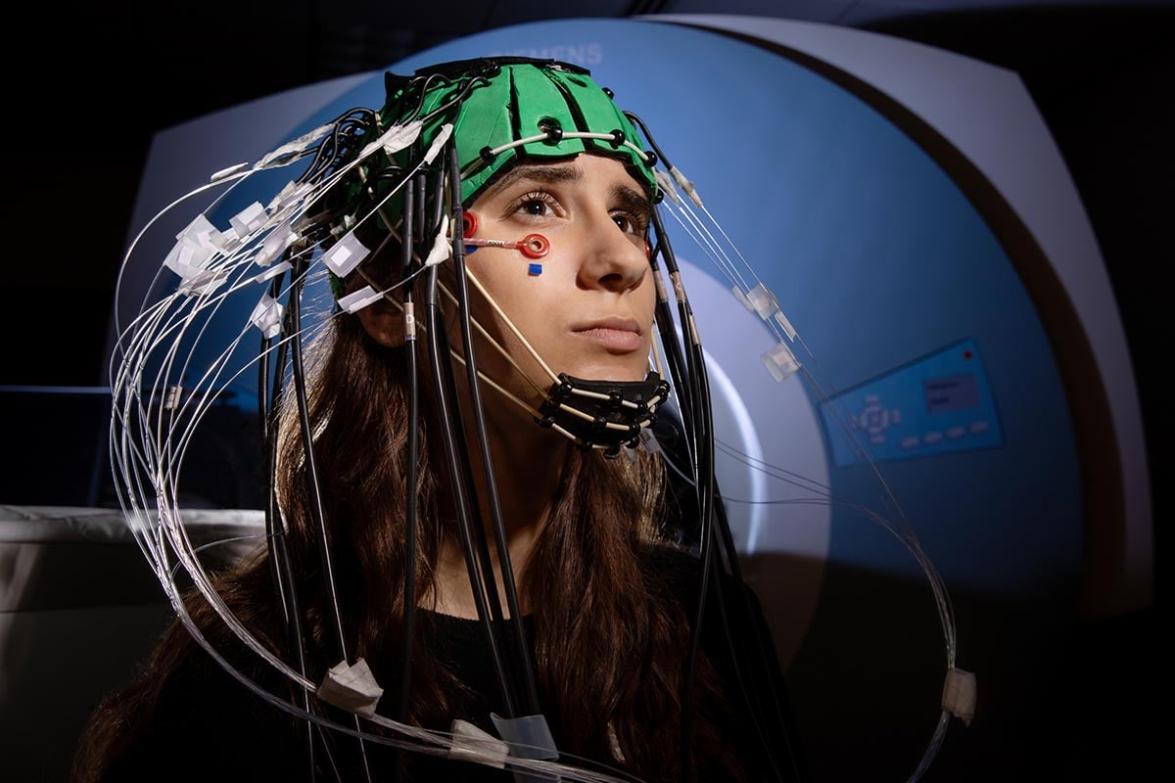

Beyond diagnosis, neuroimaging has potential applications in treatment planning, monitoring, and predicting outcomes in psychiatry.
- Treatment Planning: Neuroimaging can help clinicians tailor treatment plans based on an individual's unique brain abnormalities.
- Treatment Monitoring: Neuroimaging can be used to monitor treatment response and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Predicting Outcomes: Neuroimaging may help predict treatment outcomes and identify individuals at risk of relapse.
Future Directions And Ethical Considerations
Ongoing advancements in neuroimaging technology, such as higher-resolution scanners and improved image analysis techniques, hold promise for further enhancing the utility of neuroimaging in psychiatry.
However, ethical considerations related to the use of neuroimaging in psychiatry must be addressed, including privacy concerns, informed consent, and the potential misuse of neuroimaging data.
Neuroimaging has the potential to revolutionize the field of psychiatry by providing objective biomarkers for mental illness, aiding in diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring, and deepening our understanding of the neurobiological basis of mental disorders. Continued research and collaboration are essential to unlock the full potential of neuroimaging in improving the lives of individuals with mental illness.
YesNo

Leave a Reply