How Are Brain Disorders Diagnosed?
Brain disorders are a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. They can cause a wide range of symptoms, from memory loss and cognitive impairment to movement problems and seizures. Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential for effective management of brain disorders, as it can lead to improved treatment outcomes, better quality of life, and reduced healthcare costs.
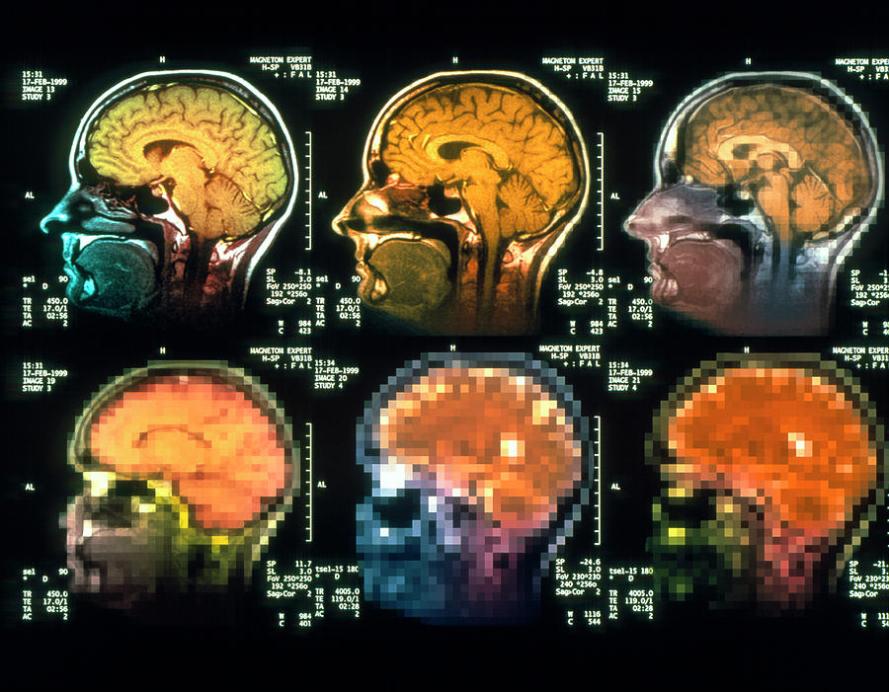
Common Brain Disorders
- Alzheimer's disease: A progressive neurodegenerative disorder that is the most common cause of dementia. Symptoms include memory loss, cognitive decline, and changes in behavior.
- Parkinson's disease: A neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement. Symptoms include tremors, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with balance.
- Epilepsy: A neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. Seizures can range from mild to severe and can cause a variety of symptoms, including loss of consciousness, convulsions, and confusion.
- Stroke: A sudden loss of blood flow to the brain. Symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the stroke, but may include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and vision problems.
- Brain tumors: Growths of abnormal cells in the brain. Symptoms can vary depending on the size, location, and type of tumor, but may include headaches, seizures, nausea and vomiting, and changes in vision or hearing.
Diagnostic Techniques
The diagnosis of brain disorders typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, neurological assessment, and various diagnostic tests.
Medical History And Physical Examination
The doctor will ask about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and family history. A physical examination will be performed to check for signs of neurological problems, such as weakness, numbness, or changes in reflexes.
Neurological Assessment
A neurological assessment is a series of tests that evaluate the patient's cognitive function, motor skills, and sensory function. This can help to identify specific areas of the brain that may be affected by a disorder.
Imaging Techniques
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. MRI can be used to identify structural abnormalities, such as tumors or strokes.
- Computed tomography (CT) scans: Use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain. CT scans are often used to diagnose strokes and brain injuries.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scans: Use radioactive tracers to measure brain activity. PET scans can be used to diagnose Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and epilepsy.
Electroencephalography (EEG) And Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
EEG and MEG are non-invasive techniques that measure brain activity. EEG measures electrical activity, while MEG measures magnetic activity. These tests can be used to diagnose epilepsy and other brain disorders that affect brain activity.
Genetic Testing And Biomarker Analysis
Genetic testing can be used to identify genetic mutations that are associated with certain brain disorders, such as Huntington's disease and some forms of epilepsy. Biomarker analysis can be used to measure levels of specific proteins or other molecules in the blood or cerebrospinal fluid that may be indicative of a brain disorder.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating between similar brain disorders with overlapping symptoms can be challenging. This is where clinical judgment, expert opinion, and multidisciplinary teams play a crucial role in accurate diagnosis.
Challenges In Diagnosis
Diagnosing brain disorders can be complex due to their heterogeneity and overlapping symptoms. Rare brain disorders pose additional challenges, as they may require specialized expertise and may be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Cultural and socioeconomic factors can also impact access to diagnosis. Individuals from underserved communities may face barriers such as lack of access to healthcare, language barriers, and cultural beliefs that may prevent them from seeking medical attention.
Importance Of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of brain disorders is crucial for effective management. Early intervention can improve treatment outcomes, enhance quality of life, and reduce healthcare costs. Public awareness and education about brain disorders and their symptoms are essential for promoting early diagnosis.
Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential for effective management of brain disorders. A combination of medical history, physical examination, neurological assessment, and various diagnostic tests is typically used to diagnose brain disorders. Differential diagnosis is important to distinguish between similar disorders with overlapping symptoms. Challenges in diagnosis exist due to the complexity and heterogeneity of brain disorders, as well as cultural and socioeconomic factors. Early diagnosis is crucial for improved outcomes and quality of life. Further research and collaboration are needed to improve diagnostic methods and outcomes for brain disorders.
YesNo

Leave a Reply