How Do Neurosurgeons Perform Brain Surgery?
Introduction:
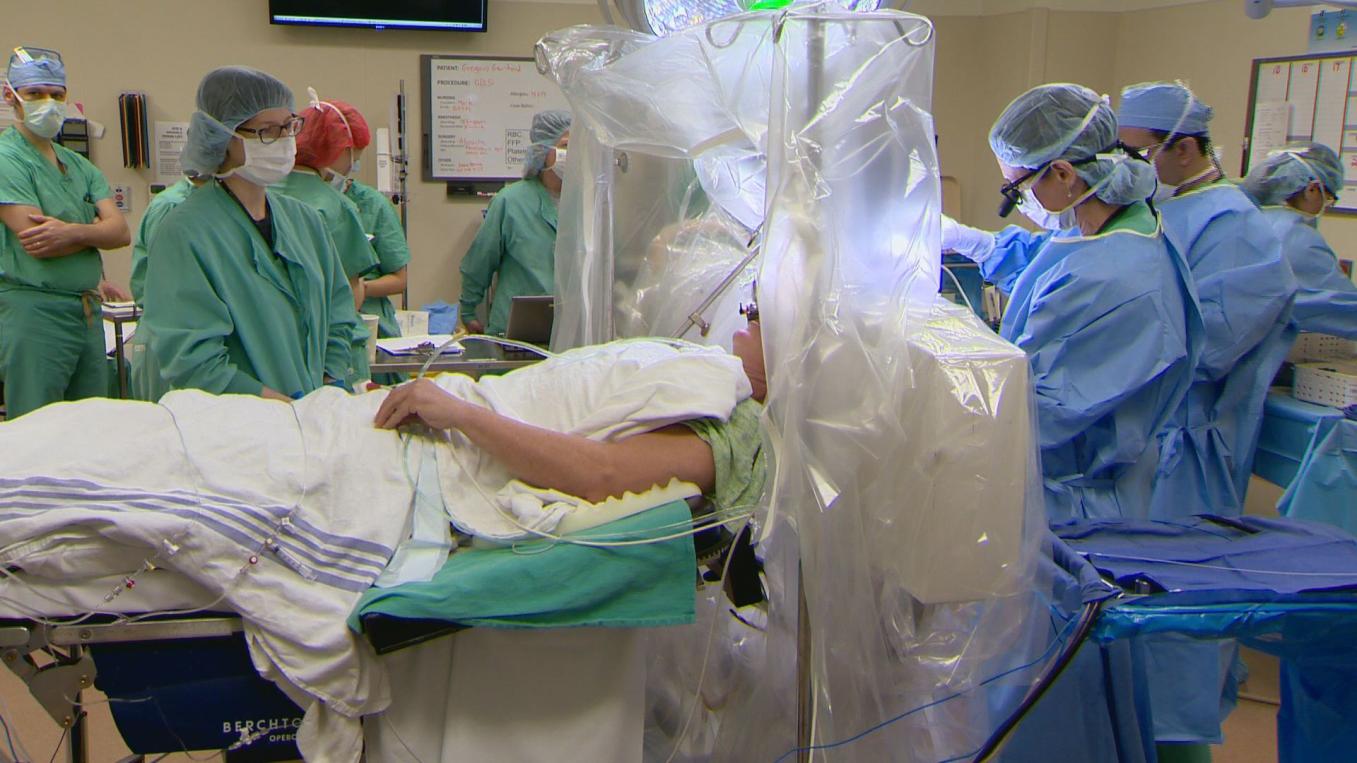
Brain surgery is a highly specialized and complex procedure that involves operating on the brain to treat various neurological conditions. It is a delicate and intricate process that requires immense skill, precision, and expertise from neurosurgeons.
Pre-Surgery Preparation:
- Patient Assessment and Diagnosis: Neurosurgeons conduct a thorough medical history and physical examination to understand the patient's condition.
- Neurological Examination: A detailed neurological examination is performed to assess the patient's neurological function and identify any deficits.
- Imaging Tests: Advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI scans, and angiography are used to visualize the brain and identify the precise location and extent of the condition.
- Anesthesia Considerations: Anesthesia is carefully administered to ensure the patient's safety and comfort during the surgery.
Surgical Procedure:
- Patient Positioning and Preparation: The patient is positioned on the operating table, and the surgical site is sterilized.
- Opening the Skull: Neurosurgeons perform a craniotomy or craniectomy to access the brain. In a craniotomy, a small portion of the skull is temporarily removed, while in a craniectomy, a larger section of the skull is removed.
- Exposing the Brain and Identifying the Target Area: Once the skull is opened, the neurosurgeon carefully exposes the brain and identifies the target area that requires treatment.
- Removing or Repairing the Affected Tissue: Depending on the condition, the neurosurgeon may remove a tumor, repair a blood vessel, or perform other necessary procedures.
- Closing the Skull and Scalp: After the surgery is complete, the neurosurgeon closes the skull and scalp using sutures or plates.
Types of Brain Surgery:
- Open Surgery (Craniotomy): This is the traditional approach where a portion of the skull is removed to access the brain.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery (Endoscopic Surgery): This involves using small incisions and specialized instruments to access the brain through natural openings or small drilled holes.
- Laser Surgery: Laser technology is used to remove or ablate targeted brain tissue with minimal damage to surrounding areas.
- Radiosurgery: This non-invasive technique uses highly focused radiation beams to target and destroy tumors or other brain lesions.
Intraoperative Monitoring:
- Neurological Monitoring: During surgery, neurosurgeons use various monitoring techniques, such as EEG and evoked potentials, to assess the patient's neurological function and prevent any potential damage.
- Blood Pressure and Oxygen Levels: Blood pressure and oxygen levels are closely monitored to ensure the brain receives adequate blood supply and oxygenation.
- Temperature Control: Body temperature is carefully regulated to prevent complications such as hypothermia or hyperthermia.
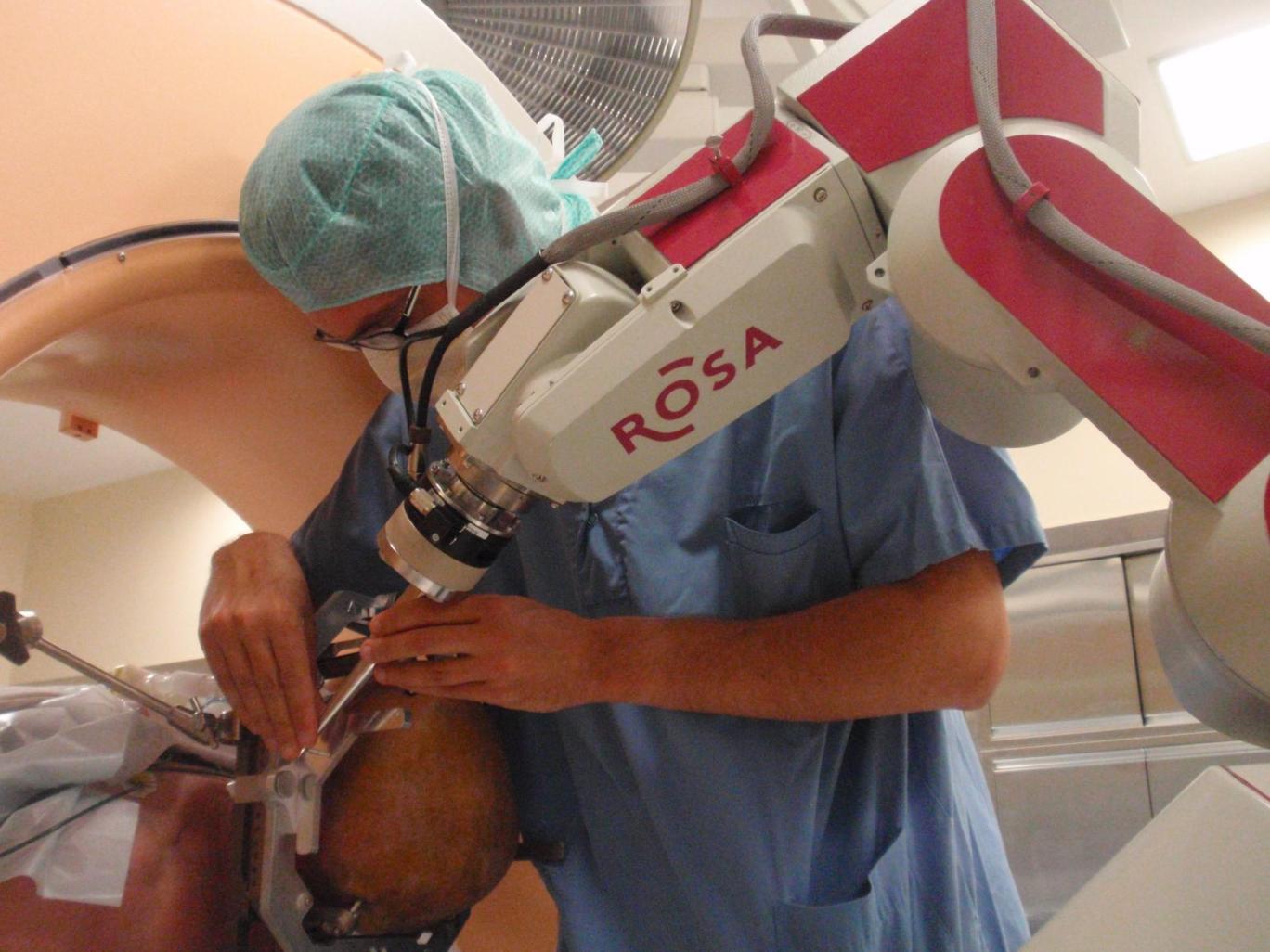
Post-Surgery Care:
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Stay: After surgery, patients are typically transferred to the ICU for close monitoring and management of their condition.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Depending on the extent of the surgery, patients may require rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain motor function, speech, or other affected abilities.
- Medication Management: Medications may be prescribed to manage pain, prevent seizures, or address other post-surgical complications.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Neurosurgeons provide long-term follow-up care to monitor the patient's recovery and provide ongoing support.
Risks and Complications:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the surgical site or within the brain.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery can lead to complications.
- Stroke: Damage to blood vessels during surgery can result in a stroke.
- Seizures: Brain surgery can sometimes trigger seizures, which may require medication.
- Cognitive Impairment: Depending on the location and extent of the surgery, there may be a risk of cognitive impairment or memory loss.
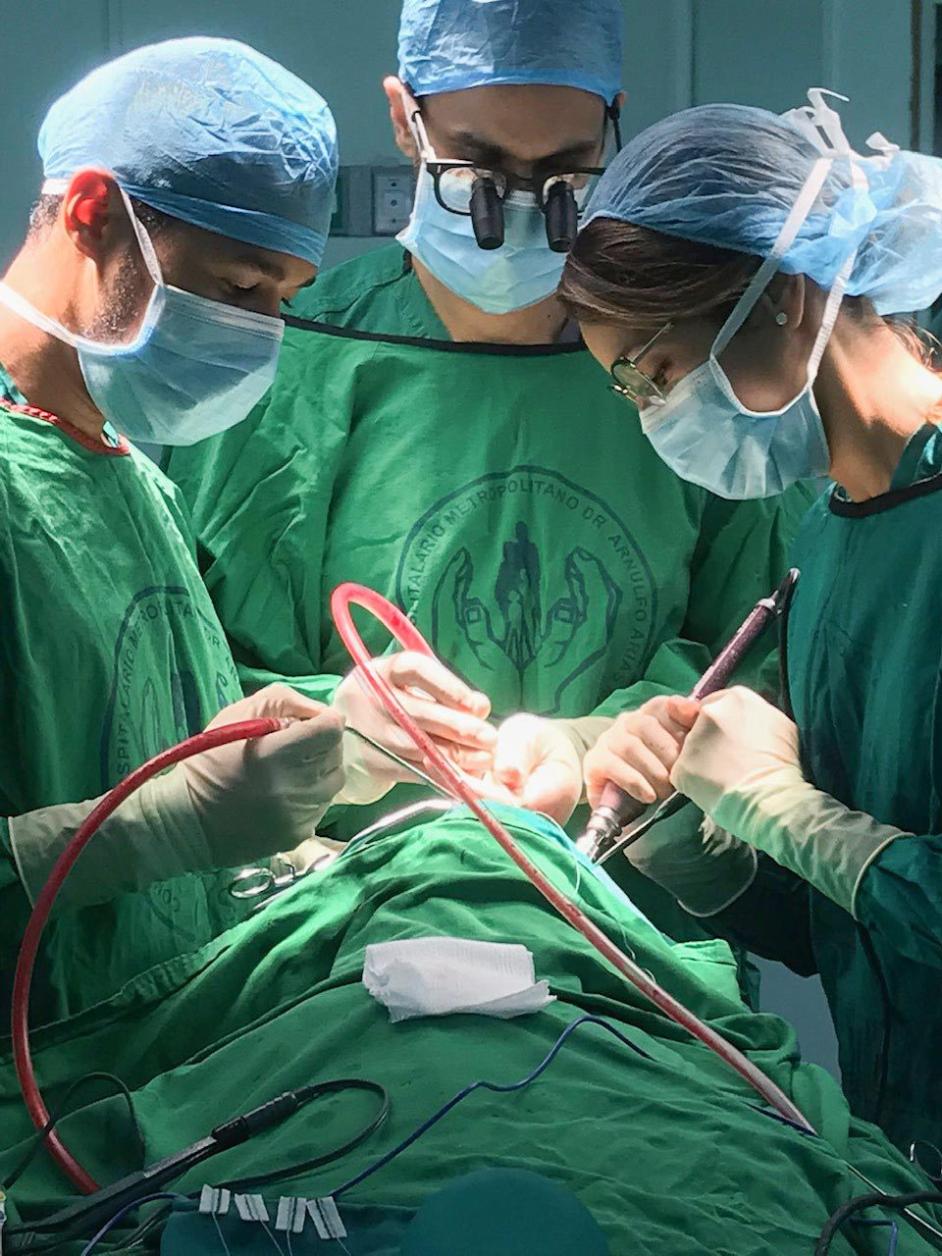
Conclusion:
Brain surgery is a complex and delicate procedure that requires immense skill, expertise, and precision from neurosurgeons. With advancements in technology and surgical techniques, the risks and complications associated with brain surgery have been significantly reduced. However, it remains a challenging and potentially life-changing procedure, and patients should carefully consider the risks and benefits before undergoing brain surgery.
YesNo

Leave a Reply