The Future of Brain Surgery: Unlocking New Frontiers in Neurosurgery
Brain surgery, a delicate and intricate field of medicine, has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years. From minimally invasive techniques to robotic assistance and gene therapy, the future of brain surgery holds immense promise for improving patient outcomes and revolutionizing the field of neurosurgery.
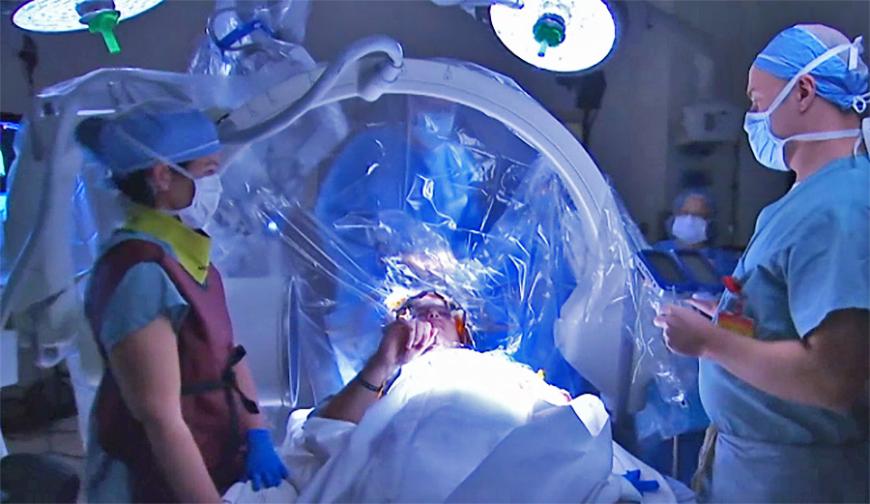
Advances In Imaging Technology
Imaging technology plays a pivotal role in brain surgery, providing surgeons with detailed insights into the brain's anatomy and pathology. Emerging imaging techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), offer unprecedented visualization of brain structures and connectivity, enabling more precise and targeted surgical interventions.
- fMRI: Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, allowing surgeons to identify functional areas and minimize damage to critical brain regions.
- DTI: Maps the direction and integrity of white matter tracts, aiding in the planning of surgical approaches and avoiding damage to essential neural pathways.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Minimally invasive brain surgery has gained significant traction due to its reduced trauma, faster recovery times, and improved patient outcomes. Keyhole surgery and endoscopic surgery are prominent examples of minimally invasive approaches, utilizing small incisions and specialized instruments to access the brain.
- Keyhole Surgery: Involves creating a small opening in the skull to access the brain, minimizing tissue damage and reducing the risk of complications.
- Endoscopic Surgery: Employs a thin, flexible endoscope inserted through a small incision to visualize and operate on brain structures, offering enhanced precision and reduced invasiveness.
Robotics And Automation In Brain Surgery
Robotics and automation are transforming brain surgery by providing surgeons with enhanced precision, stability, and dexterity. Robotic systems, equipped with advanced sensors and computer-assisted navigation, enable surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and control.
- Robotic Arms: Articulated robotic arms, guided by surgeons, can perform delicate and intricate tasks with sub-millimeter precision, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
- Automated Surgical Planning: Computer software can analyze patient data and generate detailed surgical plans, optimizing the approach and minimizing the risk of complications.
Neuro-Navigation And Surgical Planning
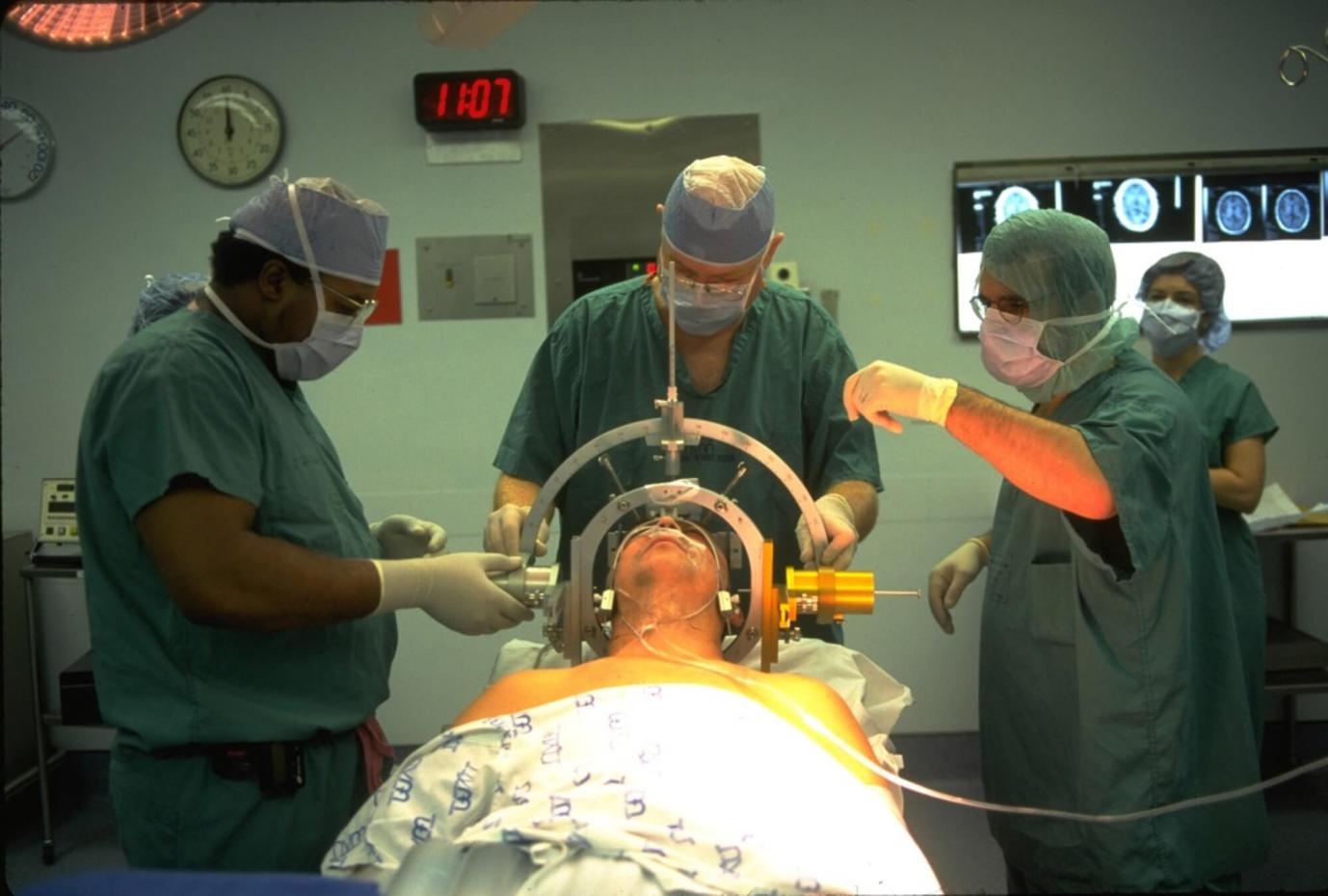
Neuro-navigation and surgical planning are essential tools in modern brain surgery, allowing surgeons to visualize the brain in three dimensions and plan the surgical approach with precision. Advanced software and imaging data are used to create detailed surgical maps, guiding surgeons during the operation.
- 3D Visualization: Surgeons can navigate through virtual representations of the brain, identifying critical structures and planning the safest and most effective surgical pathway.
- Real-Time Tracking: During surgery, surgeons can track the position of surgical instruments in real-time, ensuring accuracy and minimizing the risk of unintended damage.
Gene Therapy And Targeted Drug Delivery
Gene therapy and targeted drug delivery hold immense promise for treating brain tumors and other neurological disorders. These approaches aim to deliver therapeutic agents directly to the affected areas of the brain, minimizing systemic side effects and maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
- Gene Therapy: Involves introducing genetic material into brain cells to alter their function or repair genetic defects, potentially leading to new treatments for brain tumors and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Utilizes nanotechnology and other advanced drug delivery systems to deliver therapeutic agents specifically to brain tumors or affected brain regions, reducing side effects and improving treatment outcomes.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a cutting-edge technology with the potential to revolutionize the treatment of neurological disorders and restore lost functions. BCIs allow direct communication between the brain and external devices, enabling patients to control prosthetics, communicate, and interact with their environment.
- Motor Control: BCIs can restore motor function in patients with paralysis or neurological disorders, allowing them to control assistive devices and regain some independence.
- Communication: BCIs can provide a means of communication for patients who have lost the ability to speak or move, enabling them to express themselves and interact with others.
The future of brain surgery is brimming with possibilities, driven by advancements in imaging technology, minimally invasive techniques, robotics, neuro-navigation, gene therapy, and brain-computer interfaces. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize the field of neurosurgery, improving patient outcomes, expanding treatment options, and restoring lost functions. As research and innovation continue to push the boundaries of brain surgery, the future holds immense promise for patients with neurological disorders and conditions.
YesNo

Leave a Reply