How Does the Brain Make Decisions?
Have you ever wondered how you make decisions, from choosing what to eat for breakfast to deciding on a career path? The brain, the complex organ that controls our thoughts, actions, and emotions, plays a crucial role in this intricate process. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of decision-making, exploring the brain regions involved, the factors that influence our choices, and the neuroscience behind it all.
The Decision-Making Process
Decision-making is the cognitive process of selecting a course of action from among multiple alternatives. It's a fundamental part of our daily lives, from mundane choices to life-altering ones. The decision-making process typically involves several stages:
- Identifying the problem or opportunity: Recognizing a situation that requires a decision.
- Gathering information and evaluating options: Seeking relevant information, considering alternatives, and assessing their potential outcomes.
- Weighing the pros and cons of each option: Evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative to determine their relative desirability.
- Making a choice and committing to it: Selecting the most suitable option and taking action to implement it.
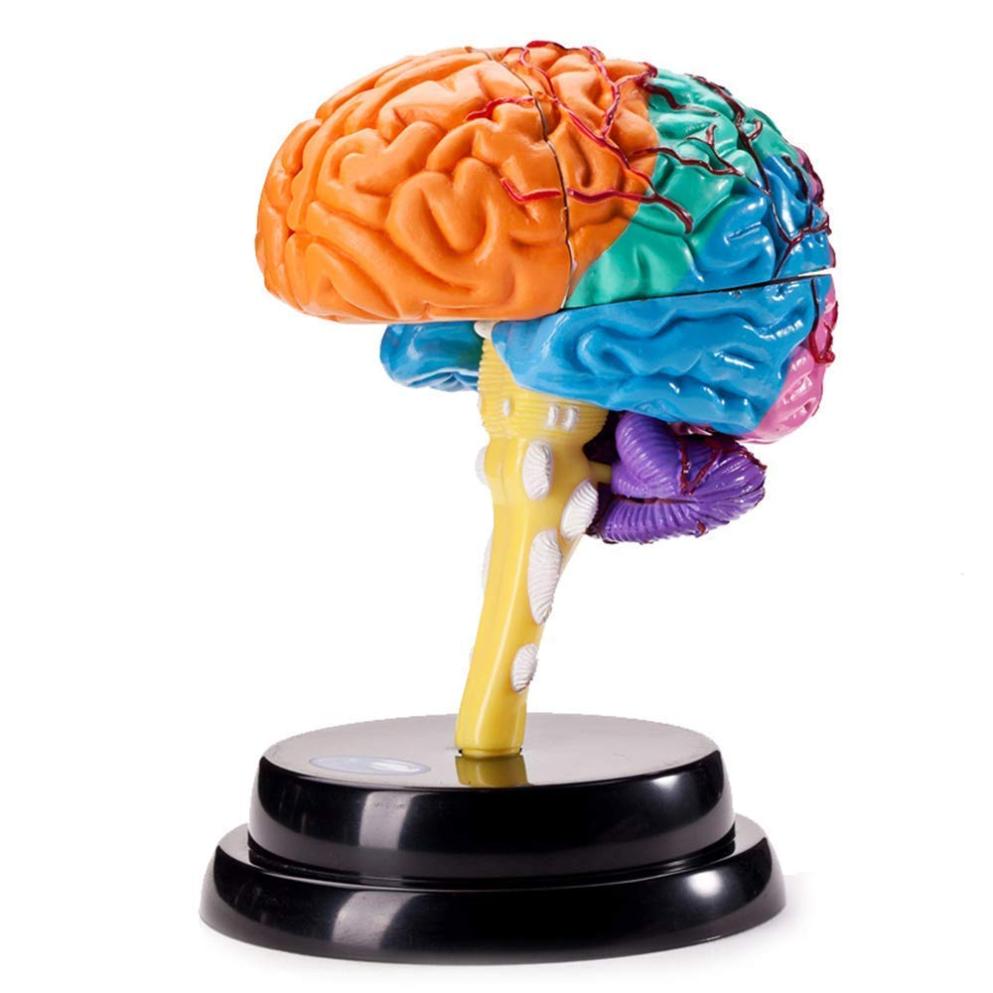
Brain Areas Involved In Decision-Making
The brain is a complex network of interconnected neurons that work together to process information and make decisions. Several brain regions are known to be involved in this process:
- Prefrontal cortex: This region is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions, including decision-making. It's involved in evaluating options, weighing pros and cons, and making choices.
- Amygdala: The amygdala is involved in emotional processing and decision-making under uncertainty. It helps us assess the emotional significance of different options and can influence our choices.
- Basal ganglia: This brain region plays a role in habit formation and decision-making based on rewards. It helps us learn from past experiences and make choices that maximize rewards.
- Hippocampus: The hippocampus is involved in memory and decision-making based on past experiences. It helps us recall relevant information and use it to make informed choices.
Factors Influencing Decision-Making
Our decisions are not made in isolation. Various factors can influence how we make choices:
- Cognitive biases: These are systematic errors in thinking that can lead to irrational decisions. Examples include confirmation bias (seeking information that confirms our existing beliefs) and anchoring bias (relying too heavily on initial information).
- Emotions: Emotions can influence decisions by providing information about potential outcomes. For instance, fear can motivate us to avoid risky choices, while excitement can drive us towards opportunities.
- Social influences: The opinions and actions of others can shape our decision-making. We may conform to group norms, seek approval, or avoid social rejection.
- Cultural and societal norms: These can influence decision-making by setting expectations and values. For example, cultural norms may influence our choices regarding marriage, career, and family.
Neuroscience Of Decision-Making

Neuroscientists study decision-making using various techniques:
- Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI): This technique measures brain activity during decision-making tasks, allowing researchers to identify the brain regions involved.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): EEG records electrical signals in the brain during decision-making, providing insights into the timing and dynamics of brain activity.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS): TMS temporarily disrupts brain activity to study its role in decision-making. By stimulating specific brain regions, researchers can investigate their causal involvement in decision-making processes.
Applications Of Decision-Making Research
Research on decision-making has practical applications in various fields:
- Improving decision-making in business, finance, and healthcare: By understanding how people make decisions, organizations can design interventions to improve decision-making processes, leading to better outcomes.
- Developing educational programs to enhance decision-making skills: Decision-making skills can be taught and improved. Educational programs can help individuals develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities.
- Designing public policies that support better decision-making: Governments can use insights from decision-making research to design policies that encourage rational and informed decision-making, leading to better societal outcomes.
The brain's decision-making machinery is a remarkable feat of nature. Understanding how the brain makes decisions not only satisfies our curiosity but also has practical implications for improving decision-making in various domains. As we continue to explore the intricacies of this process, we gain valuable insights into the human mind and its remarkable capabilities.
The question of how the brain makes decisions remains a fascinating topic, inviting further research and exploration. What are the neural mechanisms underlying different types of decisions? How do emotions and social influences interact with cognitive processes in decision-making? These are just a few of the many questions that continue to intrigue neuroscientists and psychologists alike.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the decision-making brain, we not only gain a better understanding of ourselves but also unlock the potential to improve decision-making processes, leading to better outcomes for individuals and society as a whole.
YesNo

Leave a Reply