The Science of Attention: Unraveling the Brain's Mechanisms for Focus and Resource Allocation
Attention, a fundamental cognitive process, plays a pivotal role in our ability to navigate the complexities of our environment. It allows us to focus on relevant information, filter out distractions, and allocate our cognitive resources efficiently. Delving into the science of attention provides insights into the intricate workings of the brain and its remarkable capacity for selective processing.
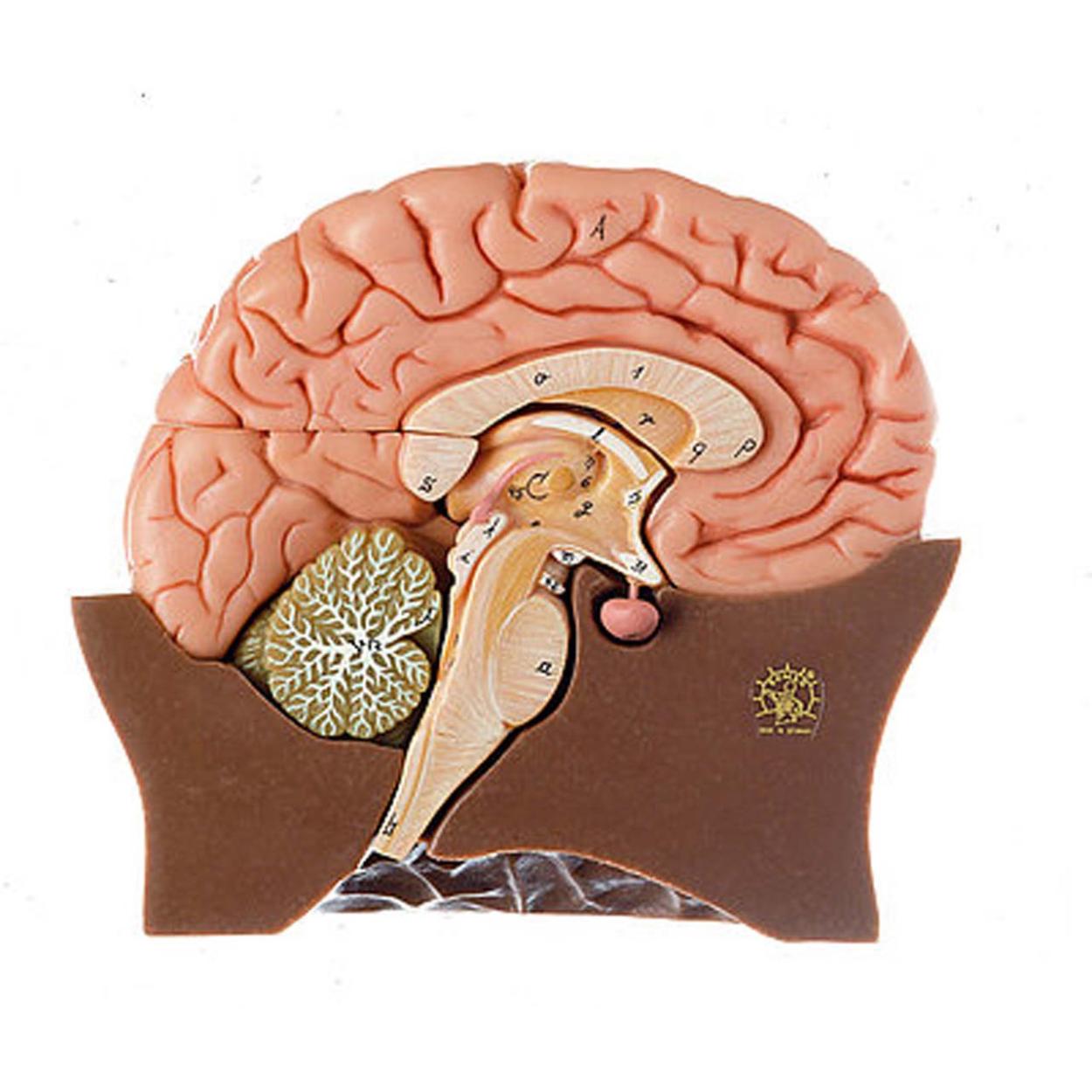
The Neuroanatomy Of Attention
The brain's intricate network of neural structures orchestrates the complex process of attention. Various brain regions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and cingulate cortex, work in concert to facilitate attentional processes.
- Frontal Lobe: The prefrontal cortex, a region within the frontal lobe, plays a crucial role in attentional control, decision-making, and working memory.
- Parietal Lobe: The parietal lobe contributes to spatial attention, directing attention to specific locations in space.
- Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe is involved in auditory attention, enabling us to focus on specific sounds amidst a cacophony of noises.
- Cingulate Cortex: The cingulate cortex is implicated in attentional orienting, helping us shift our attention between different stimuli or tasks.
These brain regions are interconnected by neural pathways, forming intricate networks that facilitate the seamless flow of information and the coordination of attentional processes.
Types Of Attention

Attention manifests in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in our cognitive repertoire.
Focused Attention
- Definition: Concentrating on a specific stimulus or task, excluding distractions.
- Selective Attention: The ability to focus on relevant information while ignoring irrelevant stimuli.
- Sustained Attention: Maintaining focus on a task over an extended period, resisting distractions.
Divided Attention
- Definition: The ability to attend to multiple stimuli or tasks simultaneously.
- Task-Switching: The ability to shift attention between different tasks or activities.
- Multitasking: Performing multiple tasks concurrently, dividing attention between them.
Voluntary and Involuntary Attention
- Voluntary Attention: Consciously directing attention to a specific stimulus or task.
- Involuntary Attention: Automatic and reflexive orienting of attention towards salient stimuli.
- Orienting Reflex: An involuntary shift of attention towards a sudden or novel stimulus.
The Mechanisms Of Attention
The brain employs various mechanisms to capture and control attention, enabling us to focus on relevant information and filter out distractions.
Attentional Capture
- Bottom-Up Processes: Stimulus-driven attention, capturing attention based on inherent stimulus properties (e.g., brightness, color, movement).
- Top-Down Processes: Goal-directed attention, influenced by our expectations, intentions, and prior knowledge.
Attentional Control
- Inhibitory Mechanisms: Filtering out irrelevant information and suppressing distractions.
- Executive Functions: Coordinating attentional resources, planning, and decision-making.
Attention And Perception
Attention plays a crucial role in shaping our perception of the world.
Selective Perception
- Focusing on relevant information while ignoring irrelevant stimuli, allowing us to perceive the world in a meaningful way.
Perceptual Organization
- Grouping stimuli into meaningful patterns, enabling us to make sense of complex sensory input.
Attention And Memory
Attention is integral to memory formation and retrieval.
Encoding
- Attention enhances the encoding of information into memory, making it more likely to be remembered.
Retrieval
- Attention influences the retrieval of information from memory, making it more accessible when needed.
Attention And Cognition
Attention is a cornerstone of cognitive processes, influencing our decision-making, problem-solving, and learning.
Attention and Decision-Making
- Attention influences the choices and judgments we make, shaping our decision-making processes.
Attention and Problem-Solving
- Attention helps us focus on relevant information and strategies, facilitating problem-solving.
Attention and Learning
- Attention enhances the acquisition of knowledge and the development of skills.
Attention And Neuroscience Disorders
Dysfunctional attentional processes are associated with various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Symptoms: Inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
- Neurobiological Basis: Deficits in attentional control and inhibitory mechanisms.
Attentional Deficits in Schizophrenia
- Symptoms: Impaired attention, difficulty focusing, and distractibility.
- Neurochemical Abnormalities: Dysregulation of dopamine and glutamate neurotransmitter systems.
The science of attention unveils the intricate mechanisms by which the brain focuses on relevant information, filters out distractions, and allocates cognitive resources. Understanding the neuroanatomy, types, and mechanisms of attention provides valuable insights into the complexities of human cognition. Further research in this field promises to deepen our comprehension of attention and its role in various cognitive processes, potentially leading to advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of attention-related disorders.
YesNo

Leave a Reply