Unraveling the Enigma of Consciousness: How the Brain Creates Our Awareness
Consciousness, the subjective experience of our own existence, is one of the most profound and enigmatic phenomena in the universe. It is the essence of our being, the foundation of our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Yet, despite centuries of philosophical and scientific inquiry, the nature of consciousness remains a mystery. How does the brain, a physical organ composed of billions of neurons, give rise to the rich and complex world of our conscious experience? This article delves into the depths of consciousness, exploring the brain structures involved, the theories that attempt to explain it, and the implications of our conscious awareness.
The Nature Of Consciousness
Consciousness is a multifaceted phenomenon that encompasses a wide range of subjective experiences, from the simple awareness of our surroundings to the intricate tapestry of our thoughts and emotions. Defining consciousness is a challenging task, as it is inherently subjective and cannot be directly observed or measured.
- Defining Consciousness: Subjective Awareness and Qualia
- Levels of Consciousness: Waking, Dreaming, and Altered States
- The Hard Problem of Consciousness: Explaining Subjective Experience
Consciousness is characterized by subjective awareness, the ability to experience the world from our own unique perspective. This includes our thoughts, feelings, sensations, and perceptions. Qualia, the subjective qualities of conscious experience, such as the taste of coffee or the beauty of a sunset, are a fundamental aspect of consciousness.
Consciousness exists in different states, ranging from the waking state to dreaming and various altered states induced by meditation, psychedelic substances, or certain neurological conditions. These altered states offer glimpses into the plasticity and malleability of consciousness.
The hard problem of consciousness is the challenge of explaining how physical processes in the brain give rise to subjective experience. This is considered one of the most difficult problems in science, as it requires bridging the gap between the objective world of physics and the subjective world of consciousness.
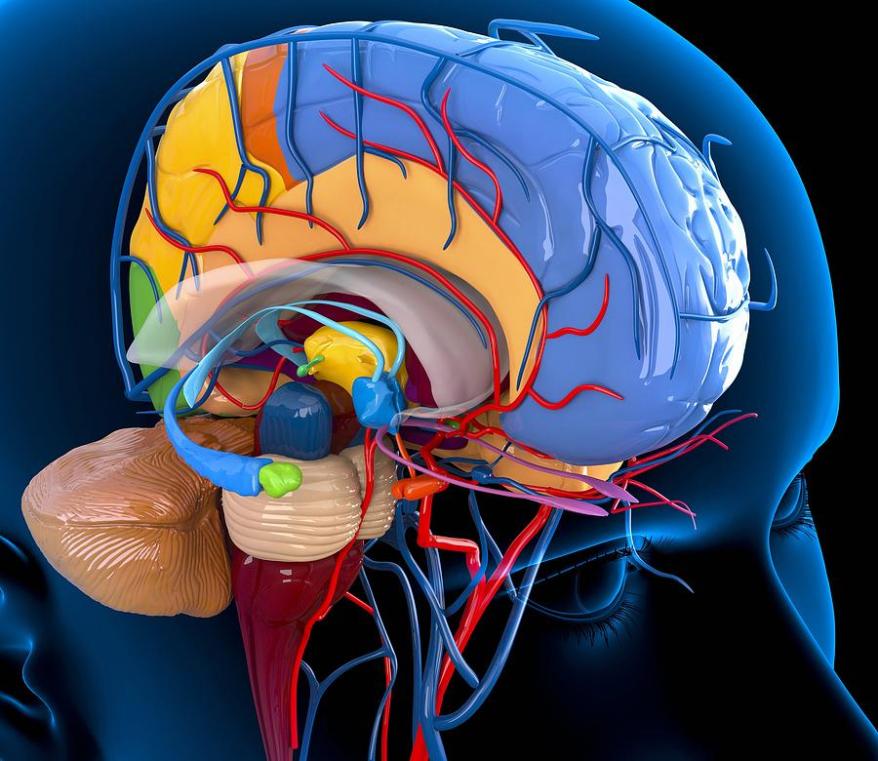
The Brain's Structures Involved In Consciousness
While the exact neural mechanisms underlying consciousness are still being investigated, certain brain structures have been implicated in its generation and modulation.
- The Cerebral Cortex: The Seat of Higher Cognitive Functions
- The Thalamus: The Gateway to Sensory Information
- The Brainstem: The Regulator of Basic Life Functions
The cerebral cortex, the outermost layer of the brain, is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as perception, attention, memory, and language. It is believed to play a crucial role in integrating sensory information and generating conscious awareness.
The thalamus, a small structure located deep within the brain, acts as a relay center for sensory information. It receives sensory signals from the body and sends them to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for processing. The thalamus is also involved in regulating sleep and arousal.
The brainstem, located at the base of the brain, controls essential life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It also plays a role in regulating consciousness, as it is involved in the sleep-wake cycle and arousal.
Theories Of Consciousness
There are two main approaches to understanding consciousness: the materialist approach and the dualist approach.
- The Materialist Approach: Consciousness as a Product of Brain Activity
- Neural Correlates of Consciousness (NCC): This theory suggests that consciousness is correlated with specific patterns of neural activity in the brain. By studying these neural correlates, scientists hope to gain insights into the mechanisms underlying consciousness.
- Integrated Information Theory (IIT): IIT proposes that consciousness is an emergent property of complex systems, such as the brain, that exhibit high levels of integrated information. According to IIT, the more integrated the information processing in a system, the higher the level of consciousness.
- The Dualist Approach: Consciousness as a Separate Entity from the Brain
- The Mind-Body Problem: The mind-body problem is the philosophical question of how the immaterial mind can interact with the physical body. Dualists argue that the mind and body are two distinct substances that somehow interact to produce consciousness.
- Arguments for Dualism: Some philosophers and scientists argue for dualism based on the subjective nature of consciousness, the unity of consciousness, and the existence of near-death experiences and other phenomena that seem to suggest that consciousness can exist independently of the brain.
The materialist approach posits that consciousness is a product of the brain's activity. According to this view, consciousness arises from the complex interactions of neurons and neural networks in the brain.
The dualist approach argues that consciousness is a separate entity from the brain and physical matter. According to this view, consciousness exists independently of the brain and interacts with it in some way.
Altered States Of Consciousness
Altered states of consciousness offer unique insights into the nature of consciousness and its relationship with the brain.
- Dreaming: The Uncharted Territory of the Mind
- Meditation: The Path to Inner Awareness
- Psychedelic Substances: Exploring the Boundaries of Consciousness
Dreaming is a state of consciousness characterized by vivid imagery, emotions, and thoughts that occur during sleep. Dreams provide a glimpse into the subconscious mind and have been studied for their potential role in memory consolidation, problem-solving, and emotional regulation.
Meditation is a practice that involves focused attention and awareness. It has been shown to alter brain activity and induce a state of relaxation and inner calm. Meditation practices aim to cultivate mindfulness, self-awareness, and a deeper understanding of consciousness.
Psychedelic substances, such as LSD, psilocybin, and DMT, are known to induce profound alterations in consciousness. These substances can produce intense visual and auditory hallucinations, altered states of awareness, and a sense of interconnectedness with the universe. Psychedelic experiences have been studied for their potential therapeutic benefits in treating mental health conditions and promoting spiritual growth.
The Implications Of Consciousness
The nature of consciousness has profound implications for our understanding of free will, moral responsibility, the self, and the meaning of life.
- Free Will and Moral Responsibility: If consciousness is a product of brain activity, does that mean that our actions are predetermined by the physical laws governing the brain? This question has been debated by philosophers and scientists for centuries and has implications for our understanding of free will and moral responsibility.
- The Self and Personal Identity: Consciousness is intimately linked to our sense of self and personal identity. If consciousness is dependent on the brain, what happens to our self when our brain dies? Questions about the nature of the self and the continuity of consciousness after death have been pondered by philosophers and theologians throughout history.
- The Meaning of Life and the Search for Purpose: The nature of consciousness also raises questions about the meaning of life and the search for purpose. If consciousness is a fleeting phenomenon that ends with death, does that diminish the value of our existence? Or does the subjective richness of our conscious experience give life inherent meaning and purpose?
The enigma of consciousness remains one of the greatest mysteries in science and philosophy. Despite significant advances in neuroscience and psychology, the nature of consciousness continues to elude our full understanding. The ongoing journey of unraveling consciousness requires interdisciplinary research, combining insights from neuroscience, philosophy, psychology, and other fields. As we delve deeper into the complexities of the brain and the subjective world of experience, we may one day come closer to solving the hard problem of consciousness and gaining a profound understanding of our own existence.
YesNo

Leave a Reply